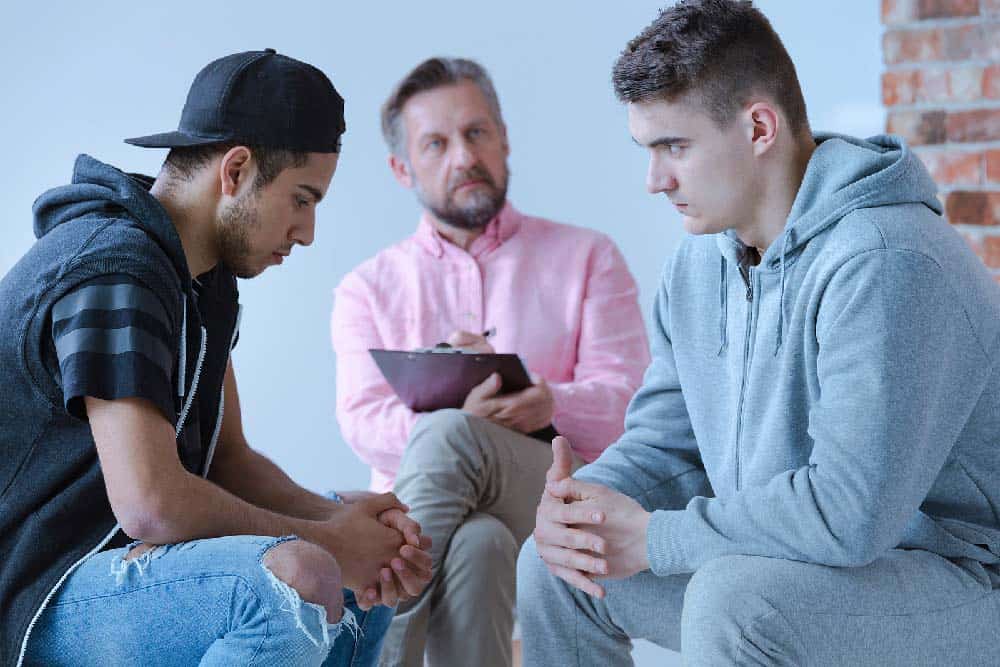
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) refers to mental health counseling with the aim of treating feelings and negative thoughts in addicted persons. The choice to stop addiction is a positive choice, but on the other hand, it comes with side effects some of which are not too appealing. Dealing with physical symptoms is not as difficult. The major concern arises with the treatment of mental and emotional symptoms. This is because they are not tangible. However, with some therapy and medication, it is possible to treat these symptoms.
Cognitive behavioral therapy is widely used in addiction treatment to help patients connect their feelings and thoughts to their actions. This acts as a form of psychotherapy, which modifies dysfunctional emotions, behaviors, and thoughts. It is diverse as it also offers treatment to disorders such as anxiety, bipolar disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, eating disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder as well as attention deficit disorder alongside addiction. In this treatment therapy, addiction patients experiencing any of the listed disorders will greatly benefit.
How Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Works
This therapeutic method indicates that harmful actions and emotions are not rational or logical. It concludes that individuals show these emotions and actions because of experiences or environmental factors. When working with addicts, the idea is to make the person understand why they feel the way they are and why they are acting as they are. They will stand a better chance of overcoming addiction.
The therapist specializing in cognitive behavior helps the patient to identify their negative thoughts. These thoughts appear automatically and they are based on impulse. Many times, they are caused by misconceptions or feelings of self-doubt and/or fear. The reason many people find themselves abusing drugs or alcohol, according to cognitive behavioral therapists, is that these individuals try to self-medicate and in turn find themselves dependent on the drug.
The continuous painful memories trigger the need to consume more so the therapist will help them learn how to initiate the memories rather than experience involuntary memories. They will, in turn, be able to reduce the effects the memories have on them. This means that they will learn how to trigger positive thoughts.
Therapists incorporate techniques such as thought records, behavioral experiments, imagery based exposure, and pleasant activity schedule. Rather than substance abuse, patients understand better ways of dealing with their situation. These techniques are normally simple to execute to prevent the persons involved from giving up the treatment process.
In the initial stages of therapy, you have to work with a trained and professional therapist to master the CBT techniques effectively. However, after well-attended sessions, you can practice the techniques at home. Alternatively, you can join a group of other people with similar concerns who can motivate you by taking on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy techniques together. Addiction support groups also apply CBT techniques and principles to help encourage long-term sobriety.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Addiction Treatment
Addiction represents a pattern of behaviors, which is triggered by the substance the individual is abusing. Individuals looking to stop substance abuse will clearly indicate that they want to stop what they feel as well as what they are doing. However, they will find themselves repeating the same things in a matter of time. This involuntary behavior is what therapists want to address.
Once the therapist can identify the patterns of thoughts and the individual’s feelings, they are able to help the person change their line of thought. This is because the thoughts that caused the addictions are normally unrealistic and untrue. The idea is to help the person face reality and begin to relate to what is true and positive. By triggering positive thoughts, the individual will be comfortable thus reducing emotional distress.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps patients suffering from drug and alcohol addiction in the following ways.
- The therapist helps the individual dismiss false beliefs and other negative insecurities that may be the possible reason why the person abuse drugs or alcohol
- The therapy sessions provide self-help tools to better their moods thus relieving the of emotional distress
- It also teaches effective communication skills allowing patients to talk about their concerns rather than rely on drugs to suppress their emotional pain
It is important to note that situations that trigger cravings increase the chances of a relapse. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy comes in handy in helping recovering addicts cope with triggers. The following is how to best cope with triggers according to this therapeutic technique.
- Recognize the trigger: The very first step is to identify the circumstances that lead to drug and alcohol abuse. The therapist is very thorough and precise at this stage. A wrong analysis will lead to the failure of the entire process.
- Avoid the trigger: With the help of the therapist, you will have to remove yourself from the trigger and its surrounding situations. This stage is gradual and the patient must be ready to advance. You will also know whether your analysis in the first stage was accurate as you should be able to note some progress. The therapist will help you to change your line of thought as well as raise your chances of increasing positive thoughts.
- Cope with the trigger: Coping with the triggers demands that you use Cognitive Behavioral Therapy techniques to alleviate your emotions. A happy person will find it easier to avoid substance abuse if it was because of negative energy and emotions.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy principles come in handy if substance abuse is caused by stressful experiences in the past, especially in cases where the person involved was disappointed or hurt. The tendency is to lean towards drug abuse to feel better. Since people react to situations differently, it is important to guide patients individually with positive thoughts to help make the treatment successful. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is part of a treatment process and it should not be used as a treatment plan on its own.