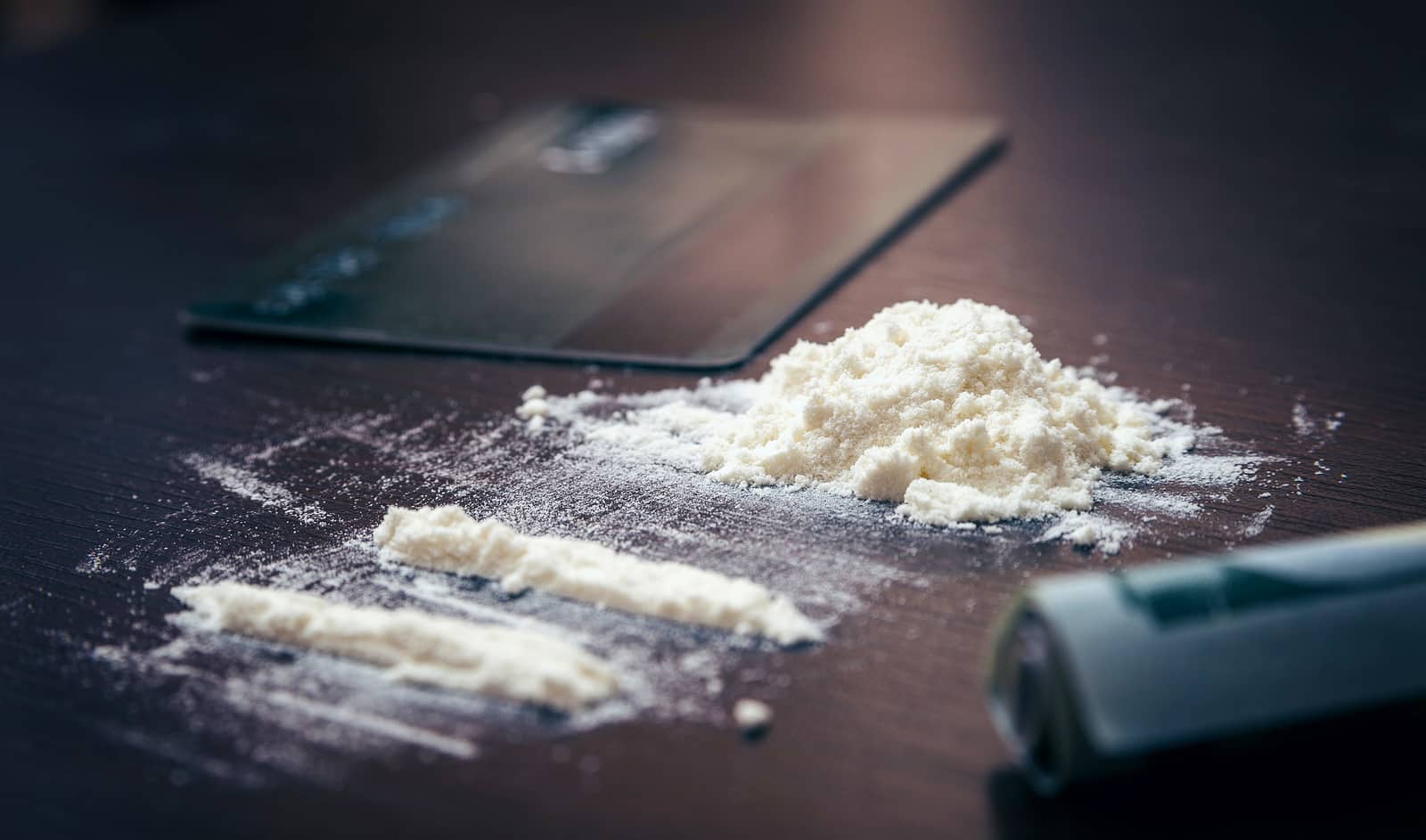
What is Cocaine?
Pronounced as /kəʊˈkeɪn/
Cocaine also known as coke is a bitter crystalline alkaloid C17H21NO4. It is a powerful stimulant drug that is very dangerous because of its high potential for drug abuse and addiction. While cocaine is illegal, it is still considered a Schedule 2 Drug in the United States. This means that even if it poses a higher risk for drug addiction, cocaine still has legal medicinal uses.
Cocaine is obtained from coca leaves (Erythroxylum coca) and is one of the oldest drugs in the world. The coca plant is native to South America and for thousands of years, people in that region have chewed and ingested coca leaves.
More than 100 years ago, the purified chemical cocaine hydrochloride was isolated from coca leaves. In the early 1900s, the purified version of cocaine became an active ingredient in tonics used to cure many different ailments. The dried coca plant leaves contain only 1% of the substance, but these leaves undergo different processes to produce the resulting cocaine white powder.
Believe it or not, this substance from the coca plant even became an ingredient in early formulations of the popular drink Coca-Cola.
Now, recreational cocaine use is widespread. Cocaine addiction is just one of the unfortunate effects of cocaine use, with many people smoking, injecting, and snorting cocaine illicitly. Cocaine overdose is also another alarming consequence for cocaine users.
What Does Cocaine Look Like?
While cocaine is usually identified as a fine white powder, this drug can actually come in different forms. Below are the different forms of cocaine: cocaine hydrochloride, crack cocaine, and cocaine sulfate.
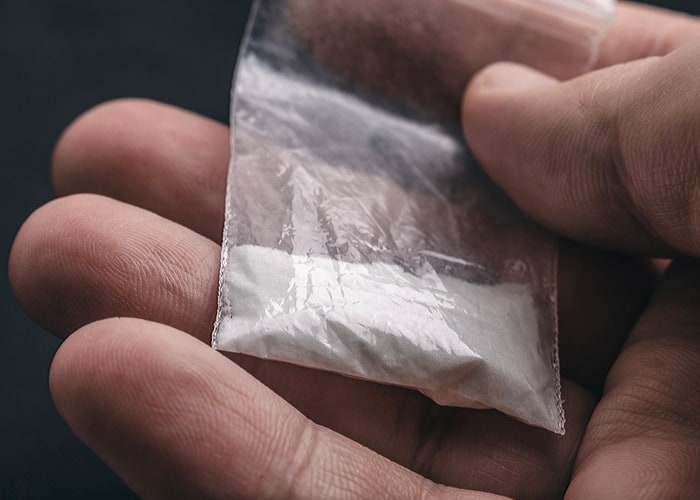

Cocaine Hydrochloride Salt (Cocaine Powder)
Cocaine hydrochloride (hydrochloride salt) appears as a fine white powder with a texture similar to talcum powder or baby powder. Just like talcum powder, cocaine powder can look like white powder. However, not all cocaine in powdered form looks like white talcum powder as the color of the drug can range from clear white, off-white, and even a yellowish or grey color depending on the levels of its purity.
The highest quality cocaine hydrochloride / cocaine powder with 98% purity is the most expensive form of the drug and looks whiter and brighter than others. Street cocaine often ranges from 5% to 40% purity because manufacturers already mix cocaine with other substances.
Cocaine use is often done by snorting cocaine or mixing it with water to inject it into the bloodstream.
Crack Cocaine
A form of cocaine that looks like rock crystal is called crack cocaine. When heated, the drug makes a crackling sound, and this crackling sound is where the term "crack cocaine" was derived.
Crack cocaine is a form of cocaine that has been processed with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and water, resulting in small solid rocks that can be smoked.
Crack is often off-white in color, but the rock crystal can also have a rosy hue that makes the drug appear pink. Crack cocaine is normally smoked in a glass pipe and crack has much stronger effects compared to cocaine powder.
Crack is also sometimes referred to as freebase cocaine, however, the two forms of the drug are actually manufactured differently even if they are both smoked. Cocaine users claim that crack is "safer" than freebasing. Both freebase and crack are often used interchangeably by cocaine users who use these drugs.

Cocaine Sulfate
This form of cocaine is also called cocaine paste. 50% of the drug is made of sulfate, but cocaine is also mixed with other chemicals such as methanol and sulfuric acid. Cocaine sulfate is also often mixed with other drugs like marijuana or tobacco and smoke.
What Are the Street Names Of Cocaine?
Cocaine has different street names. These names are used by street dealers to disguise the use of cocaine for illegal or recreational purposes.
- Basa
- Base
- Baseball
- Big flakes
- Big Rush
- Blow
- Bump
- C
- Candy
- Coke
- Cola
- Crack
- Dust
- Flake
- Gravel
- Line
- Nose Candy
- Nuggets
- Pearl
- Powder
- Rail
- Rock
- Sleet
- Snow
- Stash
- Toot
- White
- Yeyo
Crack also has its own street names. Nicknames of the drug by street dealers include the following:
- Snow coke
- Rocks
- Rock crystal
- Black rock
- Chemical
- Candy
- Nuggets
- Gravel
- Grit
- Hail
- Hard rock
- Jelly beans
- Cookies
- Dice
- Purple caps
- Scrabble
- Yam
- Sleet
- Tornado
- Freebase
What Is Cocaine Used For?
Currently, cocaine is the only drug that is both a stimulant and an anesthetic. As a stimulant, one of the effects of cocaine use is to deliver euphoria to the user. This is one of the main reason why the use of cocaine as a recreational drug or a party drug has become rampant.
When the cocaine user takes the drug, they become hyper aware but numb at the same time. Their body temperature and heart rate increase and they also have dilated pupils, extra energy, and confidence.

Some cocaine users say that the drug help them perform simple physical tasks more effectively. However, some users report that rather than helping them perform simple physical tasks, cocaine delivers the opposite effect.
Medically, cocaine as a drug has legal uses. Cocaine is used as an anesthetic or local anesthesia for surgeries including those involving the ear, nose, and throat. But due to the higher risk of cocaine addiction, the use of cocaine in contemporary medicine is highly limited. Cocaine has been replaced by other synthetic anesthetic drugs and the use of cocaine for medical purposes is strictly monitored and controlled.
How Does Cocaine Work?
As a stimulant drug, cocaine affects the brain by affecting its dopamine levels. When cocaine enters the body, the drug rapidly sends high levels of dopamine to the parts of the brain that control feelings of pleasure.
Dopamine is the “happy” neurotransmitter, a natural chemical messenger most often associated with elevating mood. Because of this, some of the effects of cocaine are alertness and instense energy. Depending on how the drug is consumed, the effects of cocaine can reach the brain quicker. For instance, smoking cocaine meakes the drug reach the bain faster compared to snorting the drug.
While cocaine is a very powerful stimulant drug, the effects of cocaine are also very short-lived. What this means is that the physical effects of cocaine use can only be felt temporarily. Depending on how you take cocaine, the euphoric effects may last for 5 minutes to 30 minutes.
How Long Does Cocaine Stay In Your System, Blood, Urine, Saliva, Hair?
If you are about to undergo a drug test, cocaine will stay in your system for some period. Use of cocaine, even just a single dose, will also be detected in your system depending on the mode of the drug test.
- Blood Test: 12 hours
- Urine Test: 8 - 24 hours
- Saliva Test: 1 – 4 days
- Hair Test: 90 days
What Are the Short-Term and Long-Term Effects of Cocaine Use?
Being a powerful drug, cocaine use significantly affects the brain and the body. People can react to the drug differently but there are common short-term and long-term effects of cocaine use.

Short term Effects of Cocaine Use:
- Increased heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature
- Erratic, aggressive behavior
- Enlarged or dilated pupils
- Narrowed blood vessels
- Heart attack, abnormal heart rhythm
- Headaches, seizures, strokes, coma
- Irritability, anxiety, restlessness.
- Paranoia
- Auditory hallucinations
- Panic
- Muscle twitches, tremors, dizziness
- Nausea and abdominal pain
- Sudden death
- Extreme sensitivity to touch, sound, and sight
- Intense happiness
- Anger/irritability
- Paranoid feeling
- Decreased appetite
- Violent behavior
- Legal problems caused by the violent behavior
- Irritation in the nasal septum
Long term Effects of Cocaine Use:
- Constricted blood vessels
- High blood pressure
- Unpredictable behavior
- Frequent panic attacks, paranoia, possible psychosis
- Profound sleep deprivation
- Irritability
- Significant weight loss, dehydration and malnourishment
- Headaches
- Bleeding into the brain
- Convulsions and seizures
- Heart disease, heart attack, and stroke
- Mood problems
- Sexual trouble
- Lung damage
- HIV or hepatitis caused by sharing needles
- Bowel decay if you swallow it
- Gastrointestinal complications
- Loss of smell, nosebleeds, runny nose, and trouble swallowing, if you snort it
- Consequences from snorting cocaine: difficulty swallowing, nosebleeds, decreased sense of smell, nasal septum irritation, hoarse throat, runny nose
- Consequences from swallowing cocaine: intestinal gangrene
- Consequences from injecting cocaine: development of deadly, allergic reactions to either cocaine or its additives, in the case of street cocaine
- Cocaine addiction and drug abuse
- Low birth weight when used by pregnant women
Dangers of Cocaine Use
Pure forms of cocaine are incredibly powerful but what makes this drug really dangerous is that it is very difficult to determine the purity of the drugs sold in the streets.
For recreational users and even experienced buyers, it is considered virtually impossible to tell the difference between pure cocaine and the version of cocaine cut with other ingredients.
What this means is that the potency and subsequent short-term or long-term effects of cocaine use can be difficult to ascertain. While weaker forms of cocaine are still damaging, not knowing the exact potency of the drug being ingested can cause unexpected adverse effects and even result in increased risk of accidental cocaine overdose.
In terms of how it affects the health, cocaine addiction could lead to dangerous side effects such as constricted blood vessels, high blood pressure, and other blood pressure problems that could lead to a heart attach, stroke and even sudden death. Instead of giving you a high, cocaine can give you the opposite effect and endanger your health.
How Does Cocaine Addiction Develop?
Cocaine is a highly addictive drug that could create psychological dependence and addiction.
In the United States, the National Survey on Drug Use and Health found that in 2015, 1 in 20 American adults ages 18 to 25 have used cocaine.
But how does cocaine addiction develop? Cocaine addiction is actually very common. Because of cocaine's euphoric effects, pleasure seekers use cocaine to get a high. The short-lived effects means that cocaine use can easily develop into a habit due to frequent doses.
Tolerance can also develop quickly with frequent doses or repeated use of cocaine, which means that users are prone to seeking higher doses to get the same intense feeling and avoid withdrawal symptoms. This habitual drug use can result in strong cravings and cocaine addiction.
What Causes Cocaine Overdose?
Taking a large amount of cocaine or any other drugs can make the body shit down including the heart and the brain. When a person takes more cocaine than his body can handle, one of the adverse effects is cocaine overdose. What is alarming is that the amount of the cocaine that could cause an overdose can vary from person to person. It can also depend on the potency of the drug being used.

Another cause of overdose is repeated drug use over a short period. Since the high delivered by cocaine use is often short-lived, users often take frequent doses to avoid withdrawal symptoms and feel high again. This type of cocaine drug use increases the risk of overdose.
Mixing cocaine with other susbtances like alcohol, heroin, opioids, and other prescription drugs should be avoided. If you mix cocaine with alcohol or heroin - this could cause an overdose.
There are different symptoms that may manifest during a cocaine overdose including the following:
- Seizures
- Convulsions
- Tremors
- Extreme agitation
- Headaches
- Chest pain
- Stomach pain
- High temperature
- Fainting
- Delirium
- Nausea/ Vomiting
- Severe Anxiety / Panic
- Paranoid Delusions or auditory hallucinations
- Fast Speech
- Increased heart rate
- Dilated pupils
- High body temperature or irregular body temperature
How Do You Treat Cocaine Overdose?
While there is no antidote to reverse cocaine overdose, emergency medical care can treat and stabilize organ functions including the lungs, heart, kidney and the body temperature. The main goal is to reduce the dangerous symptoms caused by the overdose.
For those suffering from high temperature, applying a cold compress to cool down the temperature and prevent overheating while waiting for medical assistance. For those experiencing seizures, remove pointed or sharp objects that could cause harm to the person. Some patients suffering from respiratory failure may also need CPR or respiration.
If you or someone you know is struggling with cocaine use and you suspect an overdose from these drugs, call emergency medical helpimmediately
What Are the Withdrawal Symptoms From Cocaine Drug Abuse?
Withdrawal symptoms can make it difficult to recover from cocaine addiction. Some symptoms include:
- Anxiety
- Chills
- Strong cravings for the drug
- Chest pain
- Concentration problems
- Decreased ability to feel pleasure
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Increased appetite
- Increased sleep
- Involuntary motor movements
- Muscle and bone pain
- Slowed psychomotor skills
- Suicidal thoughts
How Can You Treat Cocaine Addiction?
Repeated cocaine use and addiction can wreak havoc not only to your physical health but also in your mental state, wellbeing, relationships, career, and more. The good news is that cocaine use and addiction can be treated. There are evidenced-based modalities that can treat cocaine addiction effectively.

A comprehensive rehab program can treat cocaine addiction and also decrease the risk of relapse. This can prevent repeated cocaine use or use of other drugs after the treatment program.