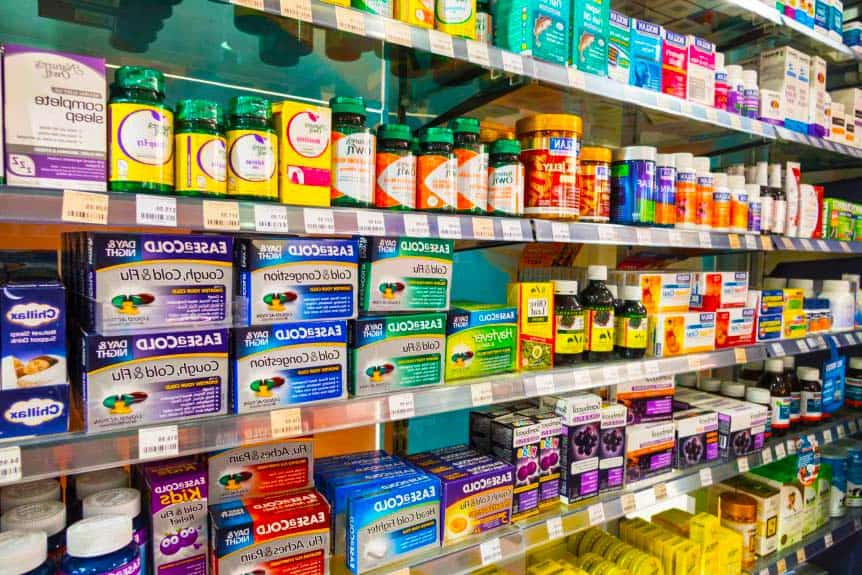
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are drugs that you can easily buy at a local pharmacy without a prescription. They are usually used for self-medicating with common health problems like colds, fever, pain, migraines, allergies, etc. The Food and Drug Administration or FDA decides which drugs are considered safe and effective enough to sell over-the-counter.
These drugs are different from health foods, dietary supplements and complementary therapies because they have been studied scientifically and extensively. The most important area of concern with these drugs is with their benefits and risks. As we all know, all drugs have certain risks that are associated with their use. These drugs have been found to have an acceptable degree of risk. To determine whether a drug is safe enough to be made available over the counter, these questions can act as a guide.
- Has the drug been used for a long enough time so that any harmful effects are fully understood?
- What harmful effects (including those from misuse) may the drug cause?
- Is the drug habit-forming?
- Do the benefits of over-the-counter status outweigh the risks?
What is the History behind Over-the-Counter Drugs?
Before there were any regulations regarding the selling of drugs, most available drugs can be bought without any prescription. Because of this, some dangerous drugs were also made available in local pharmacies that anyone can just buy. These include: alcohol, cocaine, marijuana and opium.
A set of laws called the Food, Drug, and Cosmetic (FD&C) Act, was passed by congress in 1938. These laws gave authority to the US FDA to oversee the safety of food, drugs, medical devices and cosmetics. Also in that year, the FDA formed the Drug Efficacy Study Implementation. Its job was to study and investigate the effectiveness of the drugs that were previously available in the market. In 1951, the act was amended to clarify the difference between prescription drugs and OTC drugs. They defined prescription drugs to be compounds that could be habit-forming, toxic or unsafe for use except under a doctor’s supervision. Any drug that does not fall under this category can be sold over the counter.
How Can You Ensure Safe Use of Over-the Counter Drugs?
Even though OTC drugs are relatively safe, care must still be taken when using them. Here are some tips to ensure safety and maximum effectiveness of the drug.
- Get to really know your drug – the way to do this is to read what is written on its label. The label may give you information about the right symptoms that it can cure and thus, it will help you decide if it is the right drug for you. Also, you will find in the label the instructions for its use including dosing instructions. Certain warnings may also be present on the label if it cannot be used in certain situations or conditions.
- Make sure that the drug will treat only the symptoms that you have. For example, if you have a stuffy nose, don’t take a drug that can treat headache, stuffy nose and cough at the same time. You think that this is better because it can treat more symptoms but it can also lead to certain complications or side effects if you don’t have all the symptoms that it can treat.
- Be informed about what to avoid when taking a certain over-the-counter drug. Adverse interactions with alcohol or any other substances do not only happen with prescription medicines but also with OTC drugs. Read its label for you to know what to avoid while taking it.
- Don’t be shy to ask your local pharmacist or doctor if you have questions. You have to be absolutely sure about the drug that you will take to avoid adverse side effects.
- Strictly follow the instructions on the label. Take the drug exactly how it was recommended to be taken. Be careful to strictly follow the recommended dose and frequency. A very common problem in taking OTC drugs is overdose because of not following exactly what is written on the label.
- Be very careful when taking multiple OTC drugs at the same time. You may not know that the over-the-counter drugs that you are taking have the same active ingredients that could lead to overdose without you knowing it.
- Always consult your doctor in taking any over-the-counter drug while you are still taking a prescription drug. This is because combinations of different drugs may lead to interactions that can cause unwanted side effects.
- Make sure that the drug that you are taking is appropriate for your age and weight. If a drug has restrictions with the age and weight, it would be clearly indicated on its label. This is also very important in giving kids and infants OTC drugs.
- Be sure to always check the expiration date of the drug that you are buying over the counter.
Can Over-The-Counter Drugs Be Addictive?
OTC drugs are definitely safe if taken strictly at their recommended dosages. However, they can also be abused. These drugs still pose some risk in developing addiction even if they are much less potent. This can lead to health problems including: memory loss, kidney failure, heart problems and death.
The most commonly abused OTC drugs are:
- Cough medicines (Dextromethorphan, or DMX) – these can also cause euphoric effects which make them a target for abuse. Because these are readily accessible, it makes it much easier to abuse these drugs. This can lead to vomiting, rapid heart rate, blurred vision, shakiness and even brain damage.
- Cold medicines (Pseudoephedrine) – this has an active ingredient which is also used in creating illegal drugs like methamphetamine. It is a stimulant which can cause hallucinations or an intense “body high”. Pseudoephedrine abuse cause irregular heartbeat, shortness of breath, high blood pressure, dizziness, and seizures.
- Motion Sickness Pills (Dimenhydrinate) – this drug is abused because of its psychedelic properties. Taking it in high doses can cause hallucinations, ringing in the ears, nausea, irregular heartbeat, seizures, coma, and even death.
- Pain Relievers (Acetaminomphen) – taking high doses of this drug can cause permanent liver damage, diarrhea, sweating, nausea, and stomach pain. It is often abused to treat chronic pain.
What are the Effects of Addiction to OTC Drugs?
Like with any other addictive drug, OTC drugs can also cause tolerance to the user, making them take more and more of the drug to get the same effects as when it was first used. Users may also not think of these drugs to be addictive, which can lead to more of its abuse. Since these drugs are much less potent than other addictive drugs, spotting addiction to this drug can be difficult. However, there are still signs that we can look for in determining addiction to these drugs. These are: wanting to cut back on use but being unable to do so, intense cravings to use the drug, the use of the drug is given much more priority, lack of desire to socialize, and worsening physical and psychological problems.
What are the Withdrawal Symptoms?
When the user suddenly stops taking the drug, withdrawal symptoms may also develop. These include: confusion, hostility, anxiety, mood changes.
What are the Available Treatments for those that are Addicted to OTC Drugs?
There are many treatment options that are available for individuals that are addicted to OTC drugs. These include: individual and group therapies, mental health counseling and psychotherapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). There are also rehabilitation programs that can be taken as an inpatient or an outpatient. These can all significantly help any patient on their way to complete healing and recovery from their addiction.