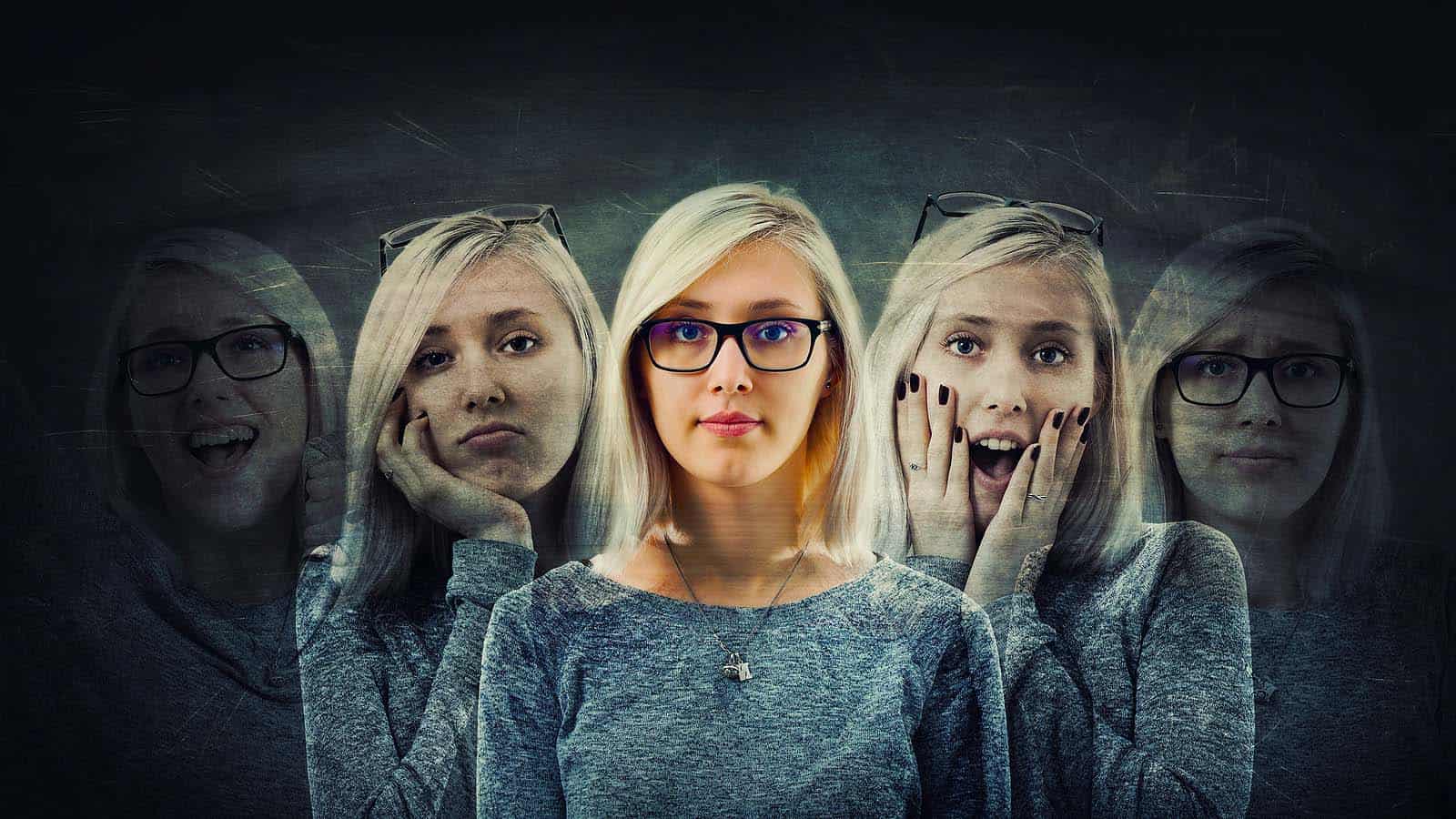
People suffering from substance abuse disorders are also experiencing other behavioral illnesses or co-occurring disorders. Oftentimes, it is almost impossible for the patient to determine if the changes in one’s behavior are due to addiction or by a co-occurring mental disorder.
What is Borderline Personality Disorder?
This is a mental condition wherein the person has difficulty in picturing out oneself and others in society. It is characterized by extreme impulsivity, intense emotions, unstable relationships, and distorted image of oneself.
One word that can be associated with a borderline personality disorder is “chaos”. Chaos because people with this condition tend to lose one’s temper easily. Aside from that, they tend to feel empty, very demanding, and experience frequent life crises.
What Is the Relationship Between Borderline Personality Disorder and Substance Abuse?
There is a silver lining between addiction and borderline personality disorder. This is true because both have similar symptoms which overlap when the two are present in an individual. Substance abuse has the capacity to magnify the negative manifestations of this condition such as anger and depression.
In the general population, approximately 1 percent are having borderline personality disorder wherein 2.7 percent are adults. Likewise, among the adults with BPD, 78 percent of them are suffering from substance abuse and alcoholism.
The three most dominant substances abused that co-occur with BPD are tobacco, alcohol, and drug abuse. Alcohol use disorder is the most prevalent while the least is drug abuse, whether illicit or medicinal substances. Approximately 57 percent of alcoholics have a co-occurring borderline personality disorder.
Overall, substance abuse and alcoholism alter the balance of behavior and mood which later progress to a borderline personality disorder. Consequently, a person with this mental disorder poses a high risk of addiction and alcoholism because of the need to balance one’s mood and feel better.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder?
A better understanding of this co-occurring behavioral disorder entails knowing the signs and symptoms of its presence. There are several manifestations of this disorder where the intensity varies to each individual.
To be diagnosed with BPD, at least five symptoms must be present since adolescence. Below are the nine common symptoms for BPD.
- Frequent paranoia and extreme skepticism of other people’s intentions.
- Inability to control anger or being extremely temperamental.
- The relentless feeling of emptiness or thinking that you do not exist in this world.
- Frequent and extreme shifts of mood episodes
- The manifestation of suicidal behavior
- Prone to doing risky and unhealthy behaviors such as unprotected sex and gambling
- Unstable sense of self
- A frequent pattern of unstable and intense relationship
- Intense fear of being left alone
Overlapping Symptoms of BPD and Addiction:
- Both show a pattern of unstable relationships
- Both show no regard for one’s health and safety
- Both show a high chance for a person to manipulate others
- Both exhibits extreme shifts of mood episodes
- Both exhibit an inability to control temper
What Are Some Triggers for Borderline Personality Disorder?
A trigger is a scenario or factor which can bring out and elevate the signs and symptoms of a certain behavioral disorder. This can either be external or internal to the patient. External triggers cannot be controlled whereas internal ones can be mitigated and prevented.
Here are the common triggers for BPD:
- Interpersonal Distress or Relationship Triggers: This happens when the person feels rejected or abandoned by the partner. It is mostly known as rejection sensitivity. This is an external trigger that cannot be entirely controlled.
Cognitive Triggers: This refers to a traumatic past experience or negative thought which suddenly pops in the head and induces the symptoms of BPD. This is an internal trigger that can be avoided through counseling and distracting oneself with hobbies and work.
How To Manage BPD Triggers?
It takes a lot of courage and support to effectively manage one’s trigger for a mental disorder. Managing a trigger for behavioral disorder incorporates three major steps.
- Identifying a Trigger: One can do this alone or through the guidance of a counselor or psychologist. The person can write these triggers in a small journal or piece of paper.
- Formulating Means to Cope with Triggers: There are several ways of formulating a healthier coping mechanism for BPD. If faced with difficulty, one can seek professional advice from a therapist or psychologist. Below are some simple and healthy means of coping with BPD.
- Listening to music
- Learning new skills and hobbies
- Maintain open communication with trusted family and friends
- Increase self-awareness and when negative emotions come in, count from 20 to 1 until it subsides
- Engage in community service and help others
- Avoiding Triggers: A person with increased self-awareness and have successfully identified one’s triggers has a greater chance of avoiding it.
In general, one must avoid events or factors which brings negative stress such as avoiding unsupportive and hot-tempered people, negative news, or any online or print media contents which drive feelings of depression, suicide, and anger.
How Common is Substance Abuse and Alcoholism Among People with Borderline Personality Disorder?
This behavioral disorder has increased prevalence among people in the United States. Below are some statistical data to describe the extent of BPD and addiction prevalence in the country.
- Among 43,000 people, 2.7 percent are diagnosed with a borderline personality disorder
- An increased risk of having this mental disorder is seen for people with the following demographics: lower income level, age 30 years and younger, broken marital relationship, and people with the lower academic achievement
- Women have a higher chance of acquiring this illness – around 75 percent
- Approximately, 63.5 percent of patients with BPD are also suffering from substance abuse and alcoholism
What Are the Treatments and Therapies of Borderline Personality Disorder?
The use of prescription drugs in the treatment of behavioral disorders are proven to be effective. However, for faster and comprehensive treatment, psychological therapies are included in the program.
Here are some of the effective psychological therapies to treat BPD:
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT): The patient undergoes training to develop effective skills to manage emotions and stress to better cope with future difficult situations in life. It can be an individual or group session.
- Schema-focused therapy: This method applies both cognitive-behavioral and psychoanalytic principles. The patient is trained to identify one’s weak spots due to emotional gaps during childhood and learn healthy coping mechanisms for them.
- Mentalization-based therapy (MBT): This method assists the patient to reflect on an emotion felt before expressing it. The patient learns to be sensitive to others and increase awareness and control of emotions.
- Transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP): This therapy enhances the patient’s interpersonal skills and understanding of one’s emotions. This is done by allowing the patient to develop a good relationship with the therapist through clarification, confrontation, and interpretation of emotions.