What is Dexedrine?
Pronounced as /ˈdeksədrən,ˈdeksəˌdrēn/
Dexedrine is the brand name for the chemical compound dextroamphetamine sulfate under the amphetamine group, specifically a sympathomimetic amine substance.
Dexedrine is one of the prescription medications used to treat ADHD or Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Dexedrine promotes focus and makes ADHD patients stay calm. Dexedrine is also used to treat narcolepsy (daytime sleepiness) as it can deliver alertness and energy for people with sleep disorders.
Dextroamphetamine sulfate is a stimulant medication that alters the actions of the endogenous catecholamines of the sympathetic nervous system (“fight or flight stimuli”). This part of the autonomic nervous system controls the body’s involuntary muscles or processes.

Because Dexedrine promotes focus and energy like other ADHD treatment medications, abuse and addiction are quite common. Dexedrine has been classified by the Drug Enforcement Agency as a Schedule II controlled substance. This means that while dextroamphetamine sulfate has a recognized medical use and can still be medically used to treat certain conditions, Dexedrine has a high potential for abuse.
What Does Dexedrine Look Like?
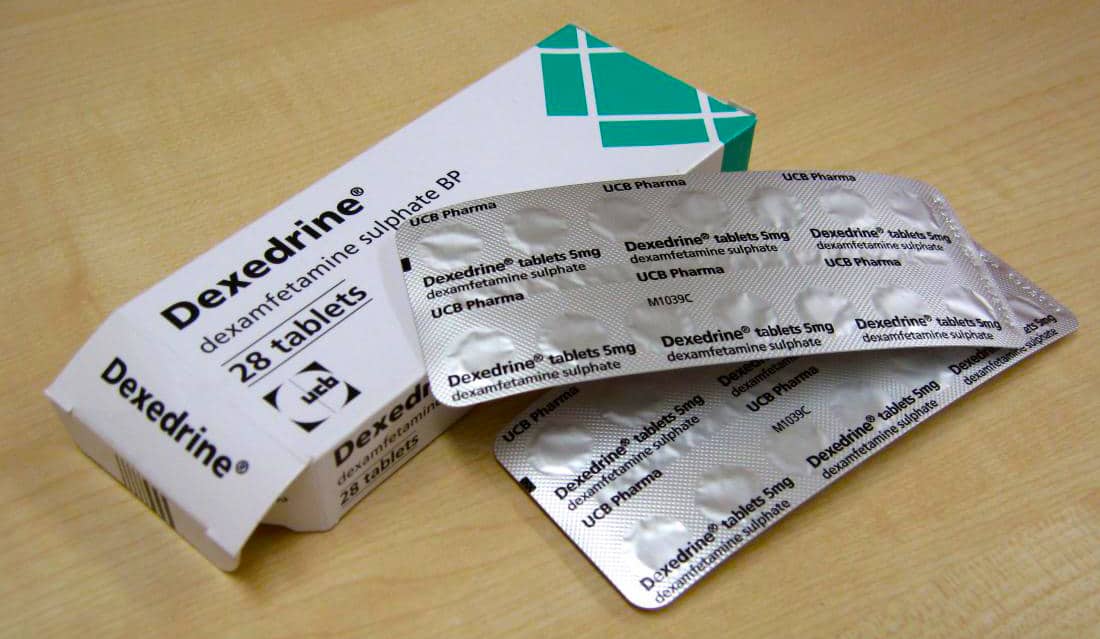
Prescription medications appear differently depending on the brand and manufacturer. For Dexedrine, it is typically sold in the market in four shapes: round, diamond, three-sides, and Spansule.

Below is a medication guide to describe the physical appearance of Dexedrine in the market.
| Name | strength | Pill Imprint | Color | Shape |
| Dexedrine | 5-mg | SKF E19 | orange | Three-sided |
| Dexedrine spansule | 5-mg | 3512 5 mg SB 5 mg | Brown | Capsule-shape |
| 10-mg | 3515 10 mg SB 10 mg | Brown | Capsule-shape | |
| 15-mg | 3514 15 mg SB 15 mg | Brown&clear | Capsule-shape | |
| Dexedrine tablet | 10-mg | 10 MIA | Peach | Round |
| 10-mg | “M” and “10” | White | Diamond | |
| 10-mg | “953 10” and “b” | Pink | Round | |
| 10-mg | U39 | Orange | Round | |
| 10-mg | N 942 | Pink | Round |
What Are the Other Names of Dexedrine?
There are other ADHD treatment medications similar to Dexedrine. Below are some of the stimulant medications with different brand names for the generic drug dextroamphetamine sulfate:
- Zenzedi
- ProCentra
- Dextrostat
What Are the Street Names of Dexedrine?
It's not uncommon for prescription medications like Dexedrine to be sold and traded illegally. Recreational users sell these stimulant medications as street drugs and call them by different names.

Street Names for Dexedrine :
- Dex
- Bennies
- Uppers
- Speed
- Beans
- Dexies
- Beauties
- Go pills
- L.A. turnarounds
- West Coast turnarounds
- Pep pills
What Is Dexedrine Used For?
Dexedrine is a sympathomimetic amine substance that is mainly used to treat ADHD. The formulation of Dexedrine aims for a gradual release of an active chemical in the blood. The effect is improved focus and stable behavior for patients taking these stimulant medications.
In addition, another use of this substance is to treat a sleep disorder called narcolepsy. Meanwhile, during the 1970s, this prescription drug was known as Obetrol and used to treat obesity.

While the drug is being used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy, Dexedrine is also used recreationally and illicitly. Take note that Dexedrine abuse and addiction can result in dangerous consequences.
How Does Dexedrine Work?
Dexedrine is a stimulant that works by altering the levels of certain natural substances in the central nervous system. Dextroamphetamine sulfate impacts the production of two neurotransmitters: dopamine and norepinephrine.
By stimulating dopamine secretion in the mesocorticolimbic system, Dexedrine can induces a euphoric feeling in the user. Meanwhile, norepinephrine gives that adrenaline effect.
Other effects include the following: inhibits mental fatigue, enhances mood, provides intense excitement, and activates the senses.
Dexedrine treats ADHD and narcolepsy by targeting the sympathetic nervous system in multiple mechanisms. These mechanisms include inhibition of the uptake of adrenergic and dopamine, enhanced secretion of monoamines, and the inhibition of monoamine oxidase.
Medication using Dexedrine induces peripheral actions and side effects such as an increase in blood pressure and enhanced respiratory action.

How Strong Is Dexedrine?
Dexedrine has a high addictive potential comparable to methamphetamines and amphetamines. It's no wonder why Dexedrine abuse is becoming more common.
In history, during World War II, the main chemical component of this medicine together with meth was used by the soldiers to keep them awake and alert always.
Dexedrine has also been classified by the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) as a Schedule II stimulant. An amount less than 15mg of this substance exhibits the same addictive level as cocaine, meth, methadone, hydromorphone, and other illicit drugs under Schedule II.
What Is the Recommended Dosage for Dexedrine?
When using this Dexedrine to treat Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy, the proper dosage must be observed to avoid any strong side effects of this substance as well as avoid the risk of Dexedrine abuse.
Below are the recommended dosages when using this drug for the medication of the two illnesses. Take note that this is only a guide and you should consult your doctor or pharmacist for a proper prescription.

Narcolepsy
The common dosage is 5-60 mg daily which is divided depending on the patient’s response to medication
First dose for 6-12 years old: 5mg per day, increments for daily dose can be 5mg per week and stop until a full response is achieved
First dose for 12 years and above: 10mg per day, increments for daily dose can be 10mg per week and stop until a full response is achieved
If you are not sure about the dose, tell your doctor first before experimenting. Only take what was written in the prescription by the doctor or pharmacist.
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
For patients ages 6 years and above: Initial dose at 5 mg once or twice a day; daily dose can be increased by 5mg per week until a full response is achieved.
A Spansule capsule formulation is not advised for administration for patients younger than 6 years.

Always follow what was prescribed by the doctor or pharmacist. If you feel that your prescribed dose is not making any effect, do not self-medicate. Tell your doctor and ask for proper advice before taking more than your current dose.
If you have a missed dose, do not double up on the next dose. Just take your next dose as usual. Doubling up on the missed dose or taking high doses could lead to a drug overdose. Call your doctor immediately for signs of overdose.
How Long Does Dexedrine Stay in Your System, Blood, Urine, Saliva, Hair?
If you are to undergo a drug test, you may be wondering how long Dexedrine stays in your system. The exact time will vary depending on the individual. The amount and how long you have been taking Dexedrine can also affect how long it stays in your system.
- Blood test: 1-2 days
- Urine test: 1-2 days
- Saliva test: 1-2 days
- Hair test: up to 90 days
What Are the Side Effects of Dexedrine?
Dexedrine can cause several side effects. Some of the common side effects may seem "attractive" to users like euphoria, energy, alertness, and wakefulness. However, the downside is that Dexedrine also causes negative side effects like increased blood pressure, circulation problems, irregular heartbeat, substance use disorder, serotonin syndrome, and more.

Dexedrine abuse and addiction can intensify these side effects and could be dangerous and possibly fatal. For instance, one of the common side effects like increased blood pressure could result in circulation problems and later on heart attack and even death.
Below are lists of the short-term side effects and long-term side effects of Dexedrine abuse. If you experience any of these side effects, tell your doctor for proper consultation.
Short-term Side Effects of Dexedrine:
- Increased blood pressure and heart rate
- Nervousness
- Inability to sleep well
- Stomach ache
- Dry mouth
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
- Being bleary-eyed or blurred vision
- Chest pain

Long-term Side Effects of Dexedrine:
- Irregular heartbeat or fast heartbeat
- Heart attack
- Blood pressure issues
- Blood flow problems or circulation problems
- Psychosis
- Cerebral hemorrhage
- High-level irritability
- Paranoia
- Sudden death
- Serotonin syndrome
- Mood swings
- Loss of sexual ability
- Physical dependence and substance use disorder
Why is Dexedrine Dangerous?
Dexedrine can be very dangerous because Dexedrine abuse is possibly fatal. Both short-term side effects and long-term side effects of this prescription drug can be dangerous, especially if users keep increasing the dosage or abusing Dexedrine.

Blood Pressure Problems
Drug abuse of Dexedrine can lead to side effects like increased blood pressure and heart rate, heart attack, cerebral hemorrhage, gastrointestinal malfunction, respiratory failure, and sudden death.
Mixing with Other Drugs
Moreover, Dexedrine abuse and pairing it with other illicit stimulants can lead to side effects like severe psychosis, chronic intoxication, and schizophrenia.
Risk for Children
In children, there is also a risk of slowing down the child's growth when using Dexedrine. If you notice side effects like problems with your child's height and weight, tell your doctor immediately.
Drug Interactions
People with the following conditions should take caution before taking Dexedrine to avoid drug interactions and severe side effects. Tell the doctor or pharmacist if you have pre-existing conditions or are taking any other prescription or over-the-counter medications.
- Blood flow problems or circulation problems
- Blood pressure and heart rate conditions like irregular heartbeat or coronary disease
- Family history of heart and blood pressure diseases
- Family history of drug abuse and addiction
- Bipolar disorder
- Allergic reactions to other amphetamines
- Thyroid problems
- Tourette's syndrome
- Using tricyclic antidepressants
How Does One Get Addicted to Dexedrine?
One of the alarming side effects of Dexedrine abuse is developing a substance use disorder or addiction to the drug. Dexedrine abuse is most common in teens and young adults. Drug abuse starts differently but often for the wrong reasons.
For instance, recreational users abuse Dexedrine to increase their focus for academic or sports achievement. Some take Dexedrine to lose weight, fight mental fatigue, or experience euphoria. There are also ADHD patients who increase their dose more than what was prescribed by the doctor or pharmacist.

The problem, however, is that Dexedrine can be highly habit-forming and addictive. In fact, the abuse and addiction potential of Dexedrine is comparable to methamphetamine and cocaine.
Repeated use of this habit-forming drug can build tolerance, which means the dosage has to be increased to get the same effect. The problem is that when you do this, you're already at a high risk of being addicted to the drug.
If you try to quit using Dexedrine on your own, you may start to experience withdrawal symptoms. These withdrawal symptoms can be painful and uncomfortable, which may cause you to use the drug again. This is one sure sign that you are already addicted to Dexedrine.
What Causes Dexedrine Overdose?
Taking too much Dexedrine can cause a drug overdose. You should not increase your dose and only use the drug as prescribed. For instance, if you have immediate-release or extended-release capsules, make sure you only take the prescribed dose or capsule.
Mixing the drug with alcohol or other drugs like opioids and benzodiazepines also increases your overdose risk. Another risk is when you get prescription drugs from street dealers or online sellers and you are not sure whether they are fake drugs. This is common especially in college campuses wherein they sell ADHD medications like Dexedrine but in reality, these are fake drugs mixed with other drugs like fentanyl. Only take Dexedrine sourced from a licensed doctor or pharmacist.
Dexedrine abuse could lead to a possibly fatal overdose resulting in side effects such as blood pressure problems such as increased blood pressure and heart rate, heart attack, serotonin syndrome, and sudden death.

What Are the Signs of an Overdose?
Dexedrine overdose can result in several symptoms which vary in intensity depending on the amount taken and frequency. To avoid dangerous consequences like sudden death, it's important to look for warning signs and call your doctor or emergency services for help.
Check out the following symptoms of Dexedrine overdose:
- Agitation
- Chest pain
- Uncontrolled body shaking
- Muscle spasms
- Overreaction to an external condition
- Death of muscle fibers
- Fast breathing pattern or trouble breathing
- Increased aggressiveness
- Hallucinations
- Panic attacks
- Blood flow problems / high blood pressure / increased blood pressure and heart rate
- Irregular heartbeat
How Do You Treat Dexedrine Overdose?
If you suspect that someone you know is struggling with a Dexedrine overdose, call your doctor or emergency services ASAP.
Do not leave the person and be ready to tell medical staff if you are aware whether the person took other drugs in addition to Dexedrine.

What Are the Withdrawal Symptoms from Dexedrine?
Withdrawal symptoms from Dexedrine may occur after a few hours after the drug was last taken, peaking 24 to 48 hours after Dexedrine use.
If you suddenly stop taking Dexedrine after abusing the drug, this could result in severe fatigue, mental retardation, and irregular sleeping patterns.
Below are some of the other evident withdrawal symptoms from Dexedrine:
- Skin diseases
- Inability to sleep
- High-level of irritability
- Intense agitation state
- Chills
- Muscle pains
- Bad dreams
- Apathy
- Mood swings
- Temporary psychosis
- Unusual tiredness or extreme tiredness
If you experience these withdrawal symptoms, tell your doctor and seek proper addiction treatment. Unfortunately, trying to deal with these withdrawal symptoms alone, you can be at risk for relapse.

How Can You Treat Dexedrine Drug Abuse and Addiction?
Dexedrine addiction is treatable. Tell your doctor or consult with an addiction specialist if you feel that you're struggling with addiction to Dexedrine or other drugs.
There are several effective methods to treat Dexedrine abuse and addiction that will address not only your physical dependence but also the root of your substance use.
These treatment options include medication-assisted treatment, cognitive behavioral therapy, psychotherapy and counseling, and holistic therapies.
Treating the person holistically allows them to find healthier ways to cope with their feelings and redirects their focus on getting well.
With the right help and support, you can recover from Dexedrine addiction.