What is Schizophrenia?
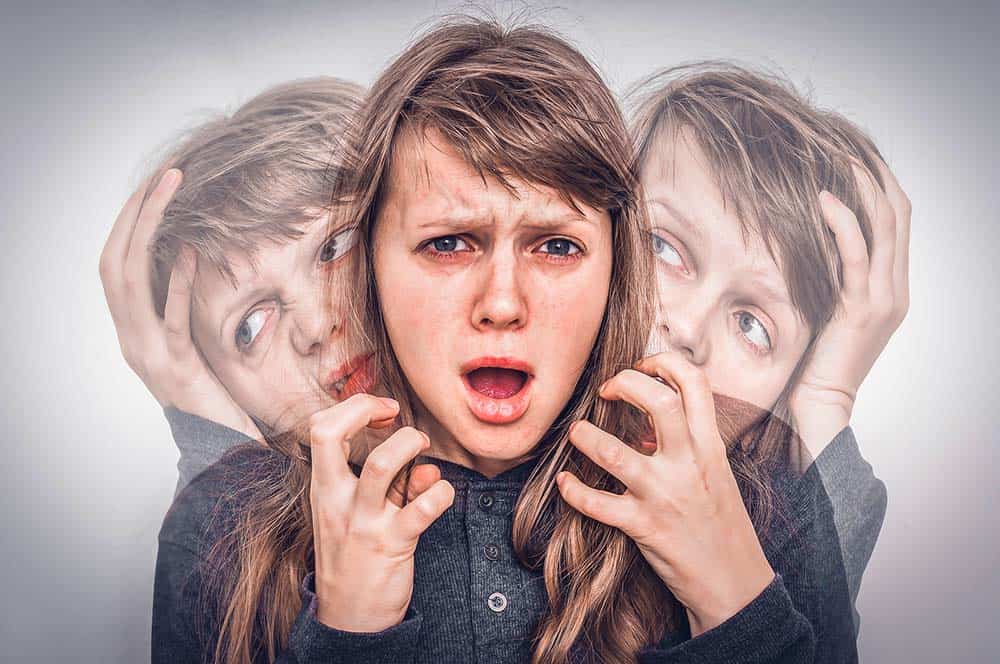
This is a mental disorder which is not that common compared to other kinds of mental diseases. People with this condition cannot properly interpret reality or has lost the sense of it. This condition impairs the proper functioning of the mind, feelings, and behavior of the patient. Likewise, this mental disorder is accompanied by hallucinations, impaired cognition, delusions, and unhealthy behaviors.
How Common is Schizophrenia in the United States?
This mental disorder is not that common unlike other diseases but it is the 15th leading factor to cause societal and economic dysfunction. Likewise, the difficulty to quantify its prevalence is highly due to its complex nature. To get a better picture of how it is affecting the United States, here are some important statistical data to take note of.
- Globally, around 1.1 percent of the general population have this disease
- Around 3.5 million people have this mental disorder in the United States
- It is the 15th leading cause of disability in the general population
- The prevalence of this disease is between 0.25 to 0.64 percent of the general population
- Approximately, 4.9 percent of people with this disease die from suicide
- In terms of economic cost, this disease costs the U.S. around $62.7 billion for health services
At What Age Do The Symptoms of Schizophrenia Start?
The two common symptoms which are hallucinations and delusions typically start at the age of 16 to 30 years old. In most cases, this disorder does not start at a very early age (below 16 years) and beyond 45 years of age. In terms of gender, it occurs at the same rate for both male and female. Likewise, there is the same probability of getting the disease from all ethnic groups.
What Causes Schizophrenia?
In most cases, there is no single factor causing this disease to happen in any person, rather, it is a combination of factors. The common factors which contribute to the progression of this mental condition include the environment, genes, and imbalances in the brain chemicals.
Environment
There are no definitive studies yet to prove that there is a solid relationship between specific social and environmental conditions and the occurrence of this mental disorder. However, most patients diagnosed with this condition experienced childhood traumatic experiences, virus infection during younger years, and stress from various events in life.
Genetics
The percentage of acquiring this disease through heredity is less than one percent but a parent diagnosed with it increases the chance to around 10 percent for the offspring.
Imbalance in Brain Chemicals
Most patients with this condition showed an imbalance of two neurotransmitters: dopamine and serotonin. The imbalance of these two brain chemicals is thought to contribute to the presence of the disease.
What Are the Symptoms of Schizophrenia?
The symptoms of this disease can start as early as 16 years of age and fully develop until the patient reaches late adulthood. The overall symptoms can be grouped into three: positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms.
Positive Symptoms:
These are psychotic behaviors manifested from the patient. These symptoms show strong signs of the person’s lost sense of reality.
- Delusions
- Hallucinations
- A distorted image of reality
- Abnormal body movements
Negative Symptoms:
These show signs of the disrupted state of behavior and emotion of the patient.
- Being emotionally numb
- Having a hard time initiating and sustaining activities
- Degraded verbal communication skills
- Reduced ability to experience happiness in life
Cognitive Symptoms:
The intensity of these symptoms can vary for different people.
- Reduced ability to comprehend and analyze information
- Difficulty to make good decisions
- Gradual memory loss
Aside from the three major symptoms, one can also observe distinct early signs and symptoms of this disorder among children and teenagers.
Early Signs and Symptoms in Childhood
- Delay in language skills
- Delay in the ability to walk
- Disrupted motor skills and behavior
Symptoms in Teenagers
- Engagement in substance abuse
- Unhealthy behaviors
- Loss of motivation
- Being highly irritable
- Depression
- Difficulty to sleep
- Social isolation
- A decline in academic performance
What Are Some Risk Factors for Schizophrenia?
It is also best that the person is aware of the risk factors that greatly contribute to the development of this mental disorder. To increase self-education, below are some of the common risk factors of this disease.
- Low nutrition level during childhood
- Viral infection
- Heredity from a family member diagnosed with this disorder
- Substance abuse during adolescence and early adulthood
- Malfunction of the immune system leading to attack its own cells
What Are Some Treatments and Therapies for Schizophrenia?
A combination of both medications and therapies is applied to patients for faster recovery. The medications aim to cure the biological aspect of mental disorder such as balancing hormones and neurochemicals. Meanwhile, the therapies target to correct unhealthy behavior and turn them into positive ones.
Medications
Most prescription drugs given to patients with this disease have an antipsychotic effect and these greatly improved treatment processes.
- Haloperidol: This drug improves clear thinking and reduces nervousness.
- Clozapine: This drug helps to regain balance in brain chemicals.
- Quetiapine: An antipsychotic drug which helps balance brain chemicals.
- Olanzapine: This drug helps the person focus and reduce the frequency of having hallucinations.
- Risperidone: This drug helps the person gain balance in mood, behavior, and brain chemicals.
Therapies
Here are some of the common and effective therapies given to patients with this disease.
- Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT): This intervention helps the patient manage and deal with hallucinations. Both the therapist and the patient formulate healthy coping mechanisms.
- Cognitive enhancement therapy (CET): This intervention helps the patient identify triggers, clear thoughts, enhance concentration, and memory. Typically, it is a combination of group therapies and computer-based cognitive exercises.
- Coordinated specialty care (CSC): This is done for patients experiencing a first-time psychotic episode. This intervention combines family support, social, and employment training to the patient in its early symptoms. An extensive treatment in the early development of the disease is important to have a bigger chance of curing and stopping the disease from progressing.
- Social skills training: This intervention aims to re-establish the social communication skills of the patient.
- Family education: The support coming from the family is a huge contributor to the treatment of this disease. This intervention educates the family about the disease and how they can help with the fast recovery of the patient.