What is Xanax?
Pronounced as /zan-aks/
Xanax is a triazolobenzodiazepine compound containing properties which can help manage anxiety and panic disorders. This is a depressant drug under the benzodiazepine class. Like any other medications under this class, it is also misused by others for recreational purposes.
The active component of this drug is alprazolam while its inactive ingredients include cellulose, starch, sodium, lactose, magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide, and sodium benzoate.
What does Xanax look like?
The drug in its purest form is a white crystalline powder which is soluble in chloroform, alcohol, acetone, ethyl acetate but insoluble in water. It produces toxic fumes of nitric oxides and hydrogen chloride when heated.
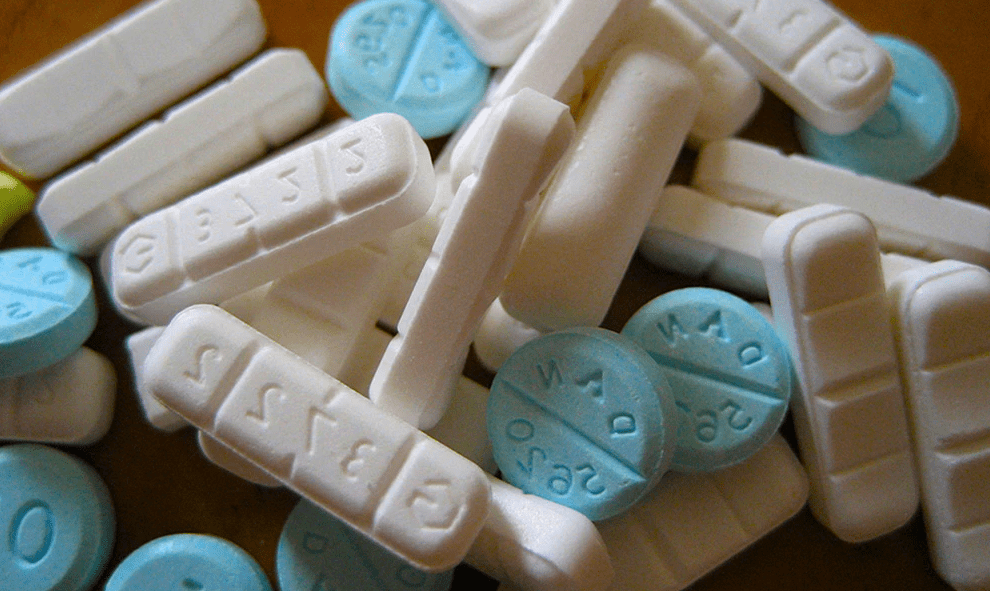
In the market, it is available in tablet forms of varying strengths: 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg of alprazolam. Below is a summary chart for the physical forms of the tablets.
Strength | Color | Shape | Imprint |
| 0.25 mg | White | Oval | XANAX 0.25 |
| 0.5 mg | Peach | Oval | XANAX 0.5 |
| 1 mg | Blue | Oval | XANAX 1.0 |
| 2 mg | White | Oblong | XANAX 2.0 |
What are the other names of Xanax?
This drug is also known by the following names:
- Alprazolam
- Trankimazin
- Tafil
- Alplax
- Constan
- Cassadan
- Esparon
- Niravam
- Frontal
What are the street names?
The drug is known in the streets by different names, depending on the area or what it is mixed with.
Here are some street names:
- Xannies
- For the 2 mg tablet: Xanbars, Handlebars, Bars, Z-bars, Totem Poles
- Zanbars
- Blue Footballs
- School bus
- Bicycle parts
- Yellow boys
- White boys
- White girls
- Footballs
- Planks
What is Xanax used for?
This prescription drug is used for the treatment and management of anxiety disorder (DSM III-R) and panic attacks (with or without agoraphobia). Anxiety disorder from everyday stress is not covered by this medication.
How does Xanax work?
This drug works on the brain and binds specifically on the benzodiazepine GABA receptor site located in the limbic system and hypothalamus. This action opens chloride channels and saturates the neurons with chloride ions which ultimately results in decreased brain activity and resistance to excitation. This gives the anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and sedative effect of the drug.
How strong is Xanax?
This drug compared to Valium is much stronger because it’s intended for the treatment and relief of severe anxiety and panic disorders. It has an intermediate onset between 15 to 30 minutes while Valium is much quicker (15 minutes). Both medications can cause withdrawal symptoms and dependency when taken at a larger dose for a longer duration. It has more side effects considering its active ingredient is much stronger. Meanwhile, when compared to Halcion, it has higher addictive potential and severe withdrawal symptoms.
How long does Xanax stay in your system, blood, urine, saliva, hair?
In comparison to chlordiazepoxide, prazepam, and clorazepate, this drug has a shorter half-life of around 6.3 to 26.9 hours with an average of 12 hours in the body. If you are to undergo a drug test, you may be wondering how long this drug stays in your system.
- Blood test: 1 to 6 days
- Urine test: 5 to 7 days
- Saliva test: up to 2.5 days
- Hair test: 1 to 7 days from the last intake but could last up to 90 days
How does one get addicted to Xanax?
This medication has a higher addictive potential than Halcion and Valium. Abuse and addiction to this drug happen when one uses it alongside with other sedatives, stimulants, alcohol and illicit substances to magnify and experience a euphoric feeling.
How does Xanax use affect the brain and the body?
The main effect of this medication is to decrease brain activity and induce muscle relaxation. It helps reduce neural transmissions which are good for patients with severe anxiety disorders. Likewise, its sedative and anticonvulsant potentials are good for the management and relief from seizures or epileptic disorders.
What are the short and long-term effects of Xanax?
Aside from the calming effect of this medication, there are other short-term and long-term effects associated with the use of this drug.
Short-term effects:
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
- Dry mouth
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Irritability
- Low sex drive
- Muscle spasm
Long-term effects:
- Seizures
- Respiratory dysfunction
- Skin problems
- Jaundice
- Hallucinations
- Depression
- Decreased motor skills
- Slurred speech
Why is Xanax dangerous?
This drug is dangerous for it has a higher potential for addiction and tolerance and is classified by the DEA under Schedule IV controlled substances. A large dose intake of this medication can lead to extreme sedation, respiratory dysfunctions, depression, paralysis, and sudden death. Further, withdrawal symptoms of this drug are much worse than Valium considering it has a stronger active metabolite.
What causes Xanax overdose?
An overdose is driven by excessive doses to get a rapid result and for recreational intentions. A prescription dose must be personalized but the general maximum daily dose must only be around 4 mg. Exceeding from that limit can cause an overdose. Likewise, ingesting it in combination with other substances to magnify the effect also leads to overdose.
What are the signs of overdose?
Here are some of the evident signs and symptoms of overdose
- Extreme sleepiness
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Impaired motor skills
- Slurred speech
- Decreased reflexes
- Muscle spasm
How do you treat Xanax overdose?
When a patient experiences a drug overdose, the following steps can be done:
- Check and monitor the patient’s vital signs
- You can do gastric lavage to remove some of the chemicals inside the stomach
- You can administer intravenous fluids
- Maintain sufficient airway for the patient
- In cases of low blood pressure, apply vasopressors
- Let the patient ingest activated charcoal to absorb some of the substances inside the body.
- Allow the patient to take flumazenil or romazicon to counteract the effect of the prescription drug.
What are the withdrawal symptoms from Xanax?
Withdrawal symptoms still occur even for prescribed doses (0.75 to 4 mg daily) and treatment duration of around 1-3 weeks. Below are some of the signs and symptoms.
Withdrawal symptoms may include:
- Intense sweating
- Seizures
- Sleeping difficulties
- Muscle spasm
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Paranoia
- Hallucinations
How can you treat Xanax addiction?
Abuse of this drug is treatable. Treatment must be done step-by-step for complete recovery. You can consider the following steps for your treatment process:
- Consult your medical personnel or clinician for a comprehensive guideline in order to recover from drug dependence.
Below are some of the drug medications to treat substance addiction:
o Flumazenil: This counteracts the effects of most benzodiazepine substances.
o Activated charcoal: It’s used to absorb some of the amounts of the drug inside the body.
o Tegretol (Carbamazepine): This calms the brain and reduces anxiety.
o Tofranil (Imipramine): This drug is under the tricyclic antidepressant group. It is used to cure depression and anxiety as a result of the addiction.
- Reward System: A contingency management plan where sets of rewards will be given to the patients who avoid using this substance.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A treatment process seeking to determine the variables causing drug abuse, risk reduction methods, and enhancing coping mechanisms.
- Recovery Group: A community-based plan which allows the patient to meet other victims and have a sharing about their experiences and success.